The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a reference model that was developed by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) providing standardization of communication between systems connected over a network. The model has seven layers which are application, presentation, session, transport, network, data link and physical. Splitting a logically into seven layers brings flexibility and adaptability of systems integrating seamlessly into the network. The model makes the components of a system plug and play. Standards are developed for each layer. The components built for each layer should comply to standard.
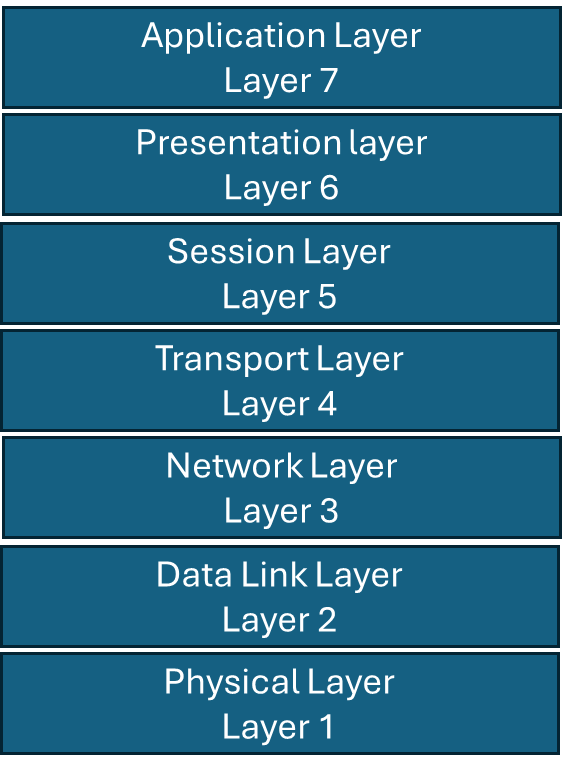
Application layer in the interface on the system that connects the end users to the network through the system. For example, a browser on a desktop allows a person to connect to the Internet and browse.
Presentation Layer does the formatting, encryption, and compression. All the data from end uses should go in a standard format across the network. ASCII, EBCDI are encoding frameworks that characters to standard format.
Session Layer is responsible for establishing, managing and terminating sessions between applications.
Transport Layer provides reliable data transfer between systems. Segmentation, error checking, flow control, and multiplexing are done in this layer. TCP and UDP are the two major protocols used for data transfer in this layer. Data conversion of information starts from this layer. The information from session layer is converted into segments. Segmentation starts from here. Headers are added starting from this layer. Ports are assigned for services and applications on Servers. Ports will be listening for requests either through TCP or UDP based on which the application is built.
Network Layer does the routing of data. The segments are converted into packets. Routing header is added to the segments. IP address in the key parameter used for routing the data to the destined to single or multiple recipients. There is a Source IP for the sender and Destination IP for the receiver.
Data Layer does the switching of data to the receiver on the physical network. The physical network can be wired or wireless. Switching header and trailer are added to the packets and converted into frames. The hardware address is used for switching. There is a Source hardware address for the sender and destination hardware address for the receiver. MAC address is the most used hardware address part of Ethernet used for LAN switching and WIFI used for Wireless networks.
Physical Layer is the last layer where the data is actually placed on the physical medium. The frames are converted into bits. The medium can be wired or wireless.
