SNMP is a protocol that is used to manage and monitor devices in IP based networks. It is used for Network Management and Network Monitoring. It collects information about the devices in a hierarchical structured way using Management Information Base (MIB).

SNMP consists of the three following components:
Managed Devices are the devices like server, routers, switches, firewalls in the organization’s infrastructure that are to be managed and monitored.
Agents are modules that run in the managed devices that gathers the information from the MIB.
Network Management Systems (NMS) are the management systems which consists of management software on a server platform with console through which the managed devices can be monitored and managed. The NMS can configure the managed devices through the Agents like configuring the IP addresses, shutting down the interfaces etc and monitor the managed devices like checking the CPU, Memory, Device health etc.
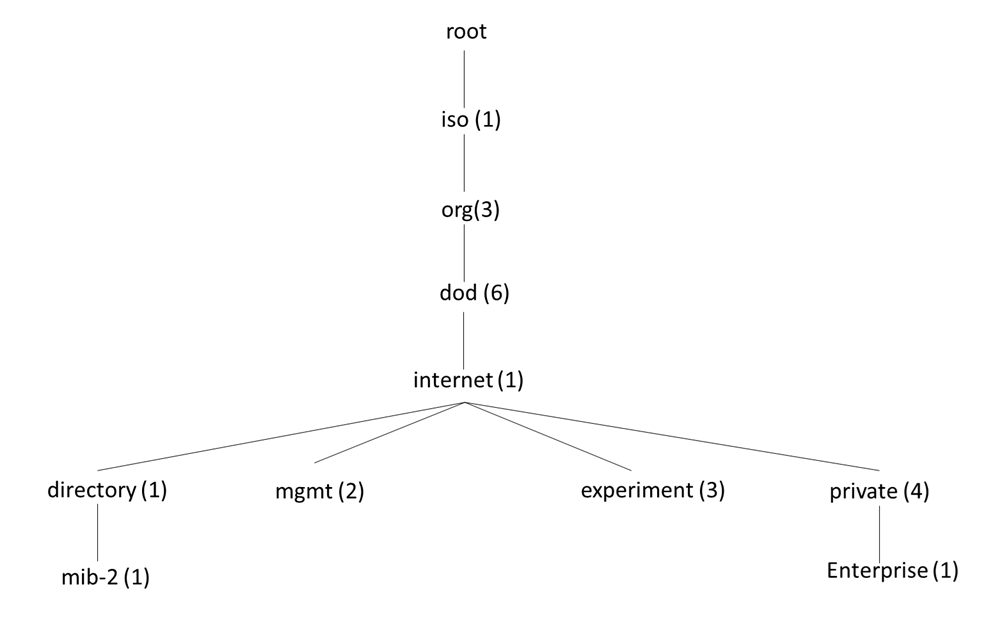
Managed Information Base (MIB) is a database that stores information of an object. An object is any parameter identified by OID of the managed device like IP address, Hostname, Domain name etc. SNMP connects to the managed device and gets the MIB data.
Object Identified (OID) are identifier used to identify objects defined by International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and ISO/IEC. The OID is structured in a hierarchical structure starting from root and moves down breaking into branches.
The following are the activities that can be performed in SNMP:
Get Request is performed by Manager and retrieves information from the variable from the Agent on the managed device.
Get Next Request is performed by Manager and retrieves information consecutively from the variable from the Agent on the managed device
Get Bulk Request is performed by Manager and retrieves information in bulk from the variables from the Agent on the managed device
Set Request is performed by Manager and sets changes to the variable in the Agent on the managed device
Response is acknowledgment response from the Agent to the Manager for the Get Request, Get Next Request, Get Bulk Request and Set Request.
Trap is notification like events, logs, alerts sent from the Agent on the Managed Device to the Manager
Inform Request is notification sent from the Agent on the Managed Device to the Manager. A acknowledgement Response is sent back by the Manager to the Agent.
SNMP Versions
SNMPv1 is the initial version of SNMP which used community strings for authentication. The NMS should know the community string to connect to the Agent to manage and monitor the device. The community string will give “Read” or Read/Write” access to the NMS. Read is only for monitoring while Read/Write provides monitoring and managing the device. The community string is weak form of authentication and made SNMP v1 weak and exploitable.
SNMPv2c made some improvements to the SNMPv1. “Get BULK Request” was introduced in this version which enabled to get bulk data from the managed devices. Inform was also introduced in this version which enabled the NMS send back acknowledgment to the notifications sent by the Agent. In the “trap”, no acknowledge was sent the NMS to the agent. But this version still used commnunity string for authentication which made it weak and exploitable.
SNMPv3 made some significant improvements in the area of Security. Instead of community strings, “username and password” – User Based Security Model (USM) was implemented for NMS authentication. Additionally, confidentiality and message integrity were which enabled encryption and integrity check for the packet. SNMPv3 can be configured between the NMS and Agent in the following three ways. In this version, an unique engine ID is provided to each entity. The device can be discovered and connected only, if the Engine ID is known.
NoAuthNoPriv – No Integrity and No Encryption
AuthNoPriv – Integrity and No Encryption
AuthPriv – Integrity and Encryption
SNMP Version Comparion
| Feature | SNMPv1 | SNMPv2c | SNMPv3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Get | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| GetNext | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Set | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Trap | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| GetBulk | No | No | Yes |
| Inform | No | No | Yes |
| Security | Community String | Community String | Username |
| Message Integration | No | No | Yes (MD5 & SHA) |
| Message encryption | No | No | Yes (AES) |
RFC References
RFC 1157 – Simple Network Management Protocol
RFC 3414 – User-based Security Model
RFC 3418 – Management Information Base (MIB) for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
RFC 3584 – Coexistence between Version 1, Version 2, and Version 3 of the Internet-standard Network Management Framework
RFC 3415 – View-based Access Control Model
RFC 5343 – Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Context EngineID Discovery
RFC 3411 An Architecture for Describing SNMP Management Frameworks
