Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol that is used in IP network to assign IP addressed to nodes connected to the network automatically. DHCP is described in RFC 2131.
In 1980s, there was Diskless Workstations which did not have disk with basic memory that used network booting. Since it has very low memory, it had to get IP addressed dynamically. Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP) a Network Protocol operating at OSI Layer 2 based on Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) was used to dynamically assign IP address to these Diskless Workstations. But RARP had major limitations that it lacked support for sending additional network configuration data apart from IP address and since it was operating at layer, it couldn’t operate across subnets.
To address the limitation of RARP, Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) was developed by researchers which assigned IP address and other network configurations like DNS, Default Gateway and Domain Name.
BOOTP was replaced by DHCP. Both uses the same port number (UDP 67 for request & UDP 68 for response). Following are major differences between DHCP and BOOTP
| BOOTP | DHCP |
| Supports limited number of client configurable options. | Supports multiple client configurable parameters using the OPTIONS parameter. |
| Doesn’t support IP renew option. | Supports IP address renew options. |
| Should be pre-configured for each client. | Pre-configuration of client is not necessary. |
| The IP address leased to clients doesn’t expire. | The IP addresses leased to client expires and are renewed. |
DHCP Header
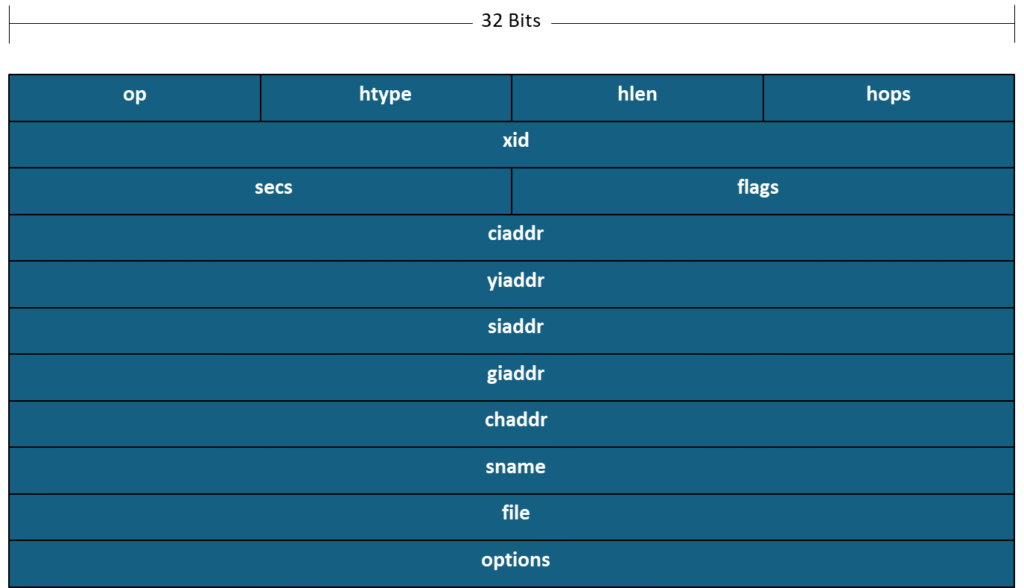
| Field | Length (Bytes) | Description |
| op | 1 | Message type set by client or DHCP Server) 1 – Boot Request (By client) 2 – Boot Reply (By Server) |
| htype | 1 | Hardware address type. Mostly, it’s 1 which is for Ethernet. |
| hlen | 1 | The length of the hardware address. It’s 6 bytes for Ethernet as MAC address is 48 bits in length. |
| hops | 1 | Set to zero by clients. If the DHCP packet passes through Relay Agent each time, this increased by 1. Every Relay agent between Client and DHCP server is considered a hop count. |
| xid | 4 | A transaction ID which is randomly selected by client and used for association between client and DHCP Server by using the same ID for all messages between them. |
| secs | 2 | Filled by client. It’s the seconds elapsed since the client obtained or renewed an IP Address. |
| flags | 2 | Only the left most bit is used and other 15 bits are set to 0. The client sets the bit 0 – DHCP Server to reply as unicast 1 – DHCP Server to reply as broadcast |
| ciaddr | 4 | The client IP address and is filled only, if the client is in Bound, RENEW and REBINDING state and can respond to ARP request. |
| yiaddr | 4 | The IP address assigned to the client by the DHCP Server |
| siaddr | 4 | The IP address of the server to be used returned in DHCPOFFER or DHCPACK from the server. |
| giaddr | 4 | The IP address of the relay device. |
| chaddr | 16 | The client hardware address which is the mostly MAC address. |
| sname | 64 | The server hostname which is optional. |
| file | 128 | The boot file name. |
| options | Variable | These are other network configuration sent by the DHCP server like domain name, default gateway. Please refer RFC 2132 DHCP Options. |
DHCP Messages
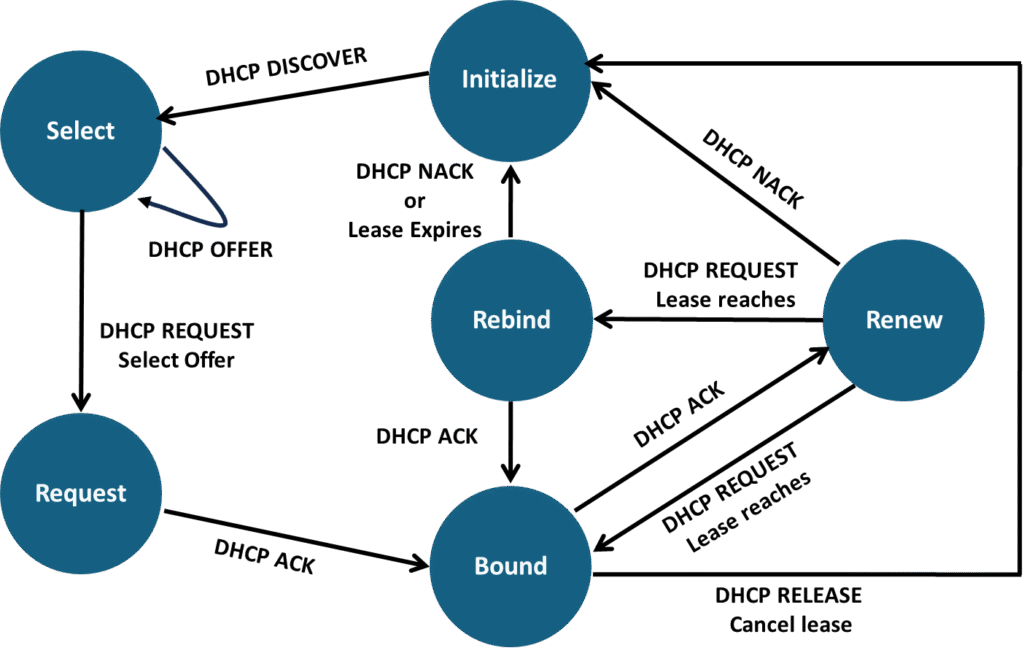
DHCPDISCOVER – The DHCP clients broadcasts a DHCPDISCOVER message to discover DHCP servers in the network.
DHCPOFFER – The DHCP server responds with DHCPOFFER message having the IP address in the “yiaddr”.
DHCPREQUEST – The client sends a DHCPREQUEST following the DHCPOFFER.
DHCPACK – The DHCP Server replies to the DHCPREQUEST sent by the client confirming the IP address request with other parameters.
DHCPNAK – The DHCP Server sends DHCPNAK when it rejects the DHCPREQUEST sent by the client.
DHCPRELEASE – The client sends a DHCPRELEASE when it wants to release the binded IP address.
DHCPINFORM – The client sends a DHCPINFORM asking for local configuration parameters when it has IP configured already externally.
DHCP Client State Diagram
Reference
RFC – 2131
RFC – 2132
